Receptor Pharmacology
Definition:
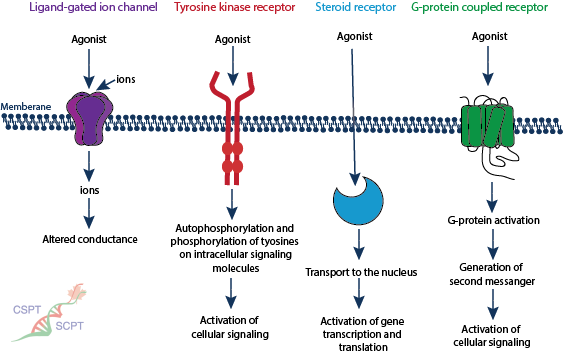
The study of the interactions of receptors with their activators, inhibitors, and other binding partners. There are five main classes of receptors: ligand-gated ion channels, drug and solute transporters (which are similar to ligand-gated ion channels when it comes to inhibitors), tyrosine kinase-coupled receptors, intracellular steroid receptors, and G-protein coupled receptors
Relevance:
Receptors are the primary target for many therapeutics as drugs can function as receptor ligands and alter physiological function to produce therapeutic responses.
Examples:
|
Receptor type
|
Ligand-gated ion channel
|
Tyrosine kinase receptor
|
Steroid receptor
|
G-protein coupled receptor
|
|
Location
|
Membrane
|
Membrane
|
Intracellular
|
Membrane
|
|
Main action
|
Ion flux
|
Phosphorylation
|
Gene transcription
|
2nd messengers
|
|
Example of receptor/drug
|
Nicotinic/Neuromuscular blocking drugs
NMDA/Ketamine
|
Insulin/Insulin
Growth factor/ EGF
|
Steroid/thyroxine
Steroid/Oestrogen
|
Opioid/Morphine
Adrenoreceptor/isoprenaline |
Return to Glossary