MetaboLite
Definition:
The product of a biotransformation reaction, often used to refer to the resulting chemical or chemicals produced from an administered drug or prodrug. The term metabolite also applies to the products of the cellular metabolism of endogenous molecules.
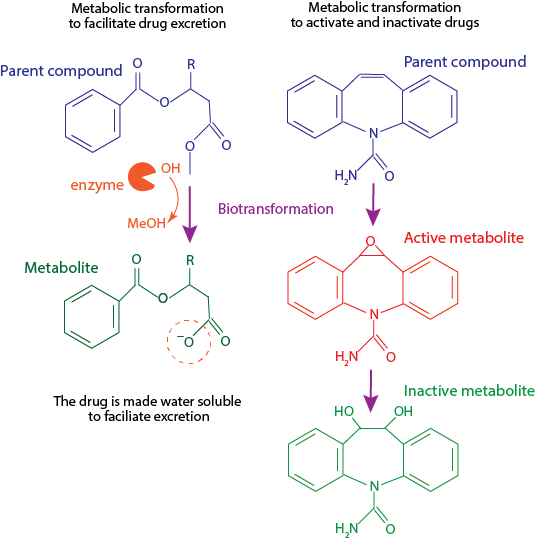
Relevance:
Biotransformation reactions may produce one or several metabolites that are less, more, or equal in activity (therapeutic or adverse) to the parent compound. For example, diazepam is metabolized into at least three metabolites, all of which are active. On the other hand, felodipine is metabolized into at least six metabolites, all of which are inactive.
Identification and characterization of a drug's metabolites are fundamental for a broader understanding of its biological effects, including its potential interactions with other medications. It is also essential for drug discovery and development as some metabolites present a better pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile than the parent drug.
Metabolites can be measured using liquid and gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and enzymatic assays. Metabolomic analysis, which measures metabolites in a biological sample via sophisticated analytical technologies, is becoming increasingly complex with the refinement of the above methods. Nonetheless, metabolomic datasets provide significant insight into the profile of a drug’s metabolites.
The detection of metabolites in biological samples has clinical and forensic relevance. For example, laboratory detection of opioids and their metabolites in the urine play an important role in identifying drug abuse and toxicity.
Linked terms: biotransformation, metabolism

